Typhoon Gaemi is a significant meteorological event. It has left a profound impact on the regions it touched, sparking discussions about climate change and geological shifts. The natural phenomenon, classified as a typhoon, swept through various parts of East Asia, caused widespread devastation, and highlighted the vulnerability of coastal areas to severe weather events.
- Typhoon Gaemi was a powerful tropical cyclone.
- It significantly impacted regions including Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and the Philippines.
- The event was a stark reminder of the ongoing climate crisis.

Historical Context of Typhoon Gaemi
Typhoon Gaemi formed in the Western Pacific Ocean, a region notorious for spawning intense tropical cyclones. As it gained strength, Gaemi’s trajectory took it towards Southeast Asia, where it made landfall with devastating consequences. The affected areas experienced torrential rains, severe flooding, and strong winds, which led to significant loss of life and property.
Geological Impact of Typhoon Gaemi
The geological impact of Typhoon Gaemi was substantial. The heavy rains triggered landslides and soil erosion in several regions, altering landscapes and causing long-term environmental damage. The intense flooding reshaped riverbeds and coastal areas, affecting both natural and human-made structures. These changes underscore the interconnectedness of geological processes and climatic events and the importance of disaster preparedness and resilient infrastructure.
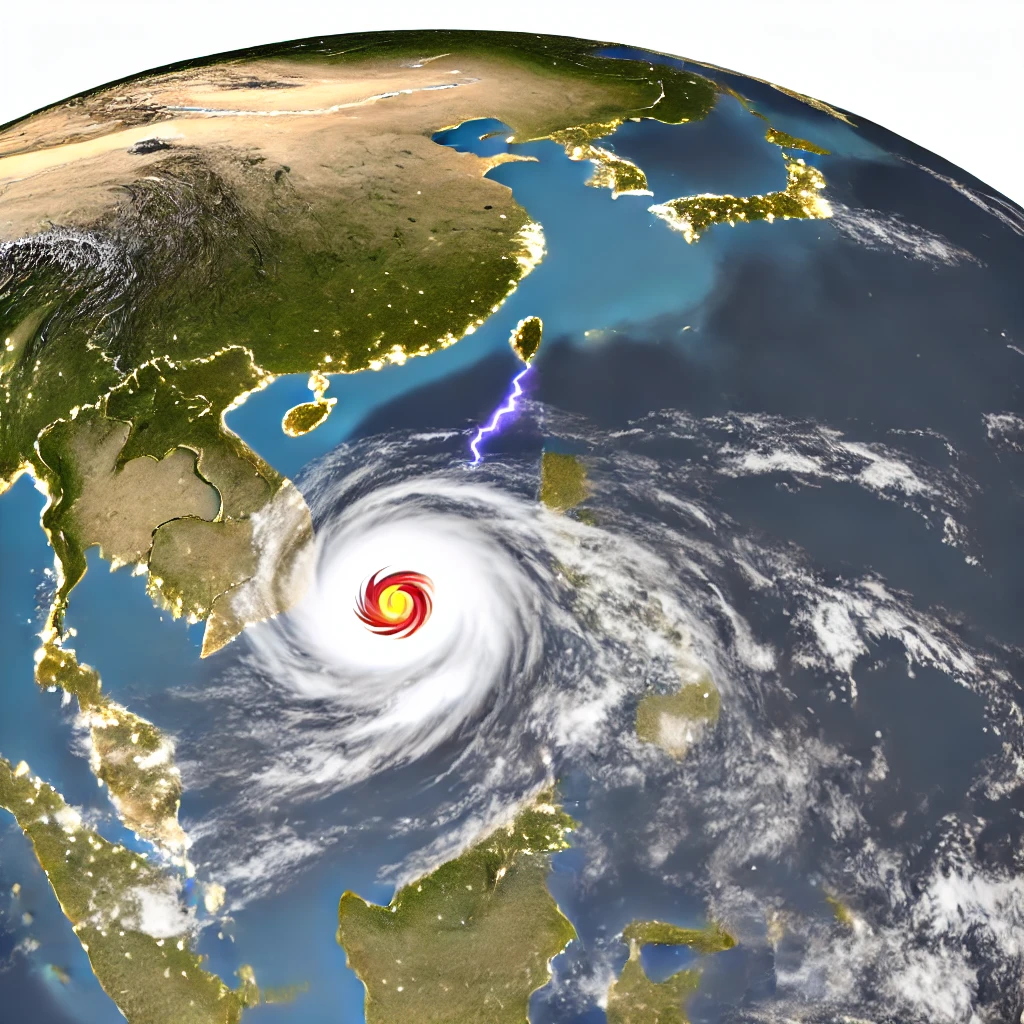
Climate Change and Typhoon Gaemi
The occurrence of Typhoon Gaemi has been linked to broader climate change trends. Warmer ocean temperatures, a consequence of global warming, are known to fuel the intensity of tropical cyclones. As sea levels rise, coastal regions become more susceptible to the impacts of storm surges and flooding. The typhoon exemplifies how climate change can amplify natural disasters, posing increased risks to vulnerable populations.
Affected Areas
Tropical cyclone Gaemi was a strong storm. It had a major effect on the Philippines, Vietnam, Thailand, and Cambodia.
Vietnam
Vietnam faced severe impacts from Typhoon Gaemi, with heavy rains leading to widespread flooding and landslides. The central and southern regions were particularly affected, with significant damage to infrastructure and agriculture. The Vietnamese government launched extensive relief efforts to aid affected communities and rebuild damaged areas.
Thailand
In Thailand, Typhoon Gaemi caused substantial disruption, especially in the northeastern and central parts of the country. Floodwaters inundated homes and farmlands, leading to economic losses and displacement of residents. The event highlighted the need for improved flood management systems and adaptive strategies to mitigate future risks.
Cambodia
Cambodia also experienced the brunt of Typhoon Gaemi’s force. The country’s already vulnerable infrastructure was further strained, with many areas suffering from prolonged flooding. The Cambodian authorities, with international aid organizations, worked tirelessly to provide relief and support to those affected by the disaster.
Philippines
The Philippines was also significantly affected by Typhoon Gaemi. The typhoon brought heavy rains and strong winds to the country, causing extensive flooding and damage to infrastructure. The agricultural sector was particularly hard hit, with many farmlands inundated and crops destroyed. The government and various non-governmental organizations mobilized resources to assist affected communities and facilitate recovery efforts.
Aftermath of Typhoon Gaemi
The aftermath of Typhoon Gaemi has provided valuable lessons for disaster management and climate resilience. It underscored the importance of early warning systems, community preparedness, and international cooperation in responding to natural disasters. The event also highlighted the need for sustainable development practices that take into account the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events due to climate change.
Typhoon Gaemi is a prime example of how climate change can exacerbate natural disasters. The typhoon’s path through Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and the Philippines brought attention to the urgent need for disaster management improvements. Flooding and landslides were among the immediate consequences, demonstrating the interconnectedness of geological processes and climate events. By studying the typhoon, scientists can better understand the importance of resilient infrastructure in mitigating future risks. The affected regions have shown remarkable resilience. However, there is a clear need for sustainable development practices to address the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events.
Relevance for UPSC Aspirants
Typhoon Gaemi serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing challenges posed by natural disasters in the context of a changing climate. The affected areas, including Vietnam, Thailand, and Cambodia, have demonstrated remarkable resilience in the face of adversity. However, we must translate the lessons learned from this event into actionable policies. As the world continues to grapple with the effects of climate change, the experiences of those impacted by Typhoon offer critical insights into building a more resilient and sustainable future.
| Typhoon Gaemi UPSC Notes |
| 1. Typhoon Gaemi was a significant meteorological event that impacted various parts of East Asia, including Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and the Philippines, causing widespread devastation. 2. The typhoon’s heavy rains led to severe flooding and landslides, particularly in the central and southern regions of Vietnam, damaging infrastructure and agriculture. 3. Thailand experienced substantial disruption from Typhoon Gaemi, with floodwaters inundating homes and farmlands, leading to economic losses and displacement of residents. 4. Cambodia’s already vulnerable infrastructure was strained by prolonged flooding, prompting extensive relief efforts by Cambodian authorities and international aid organizations. 5. The Philippines faced heavy rains and strong winds, resulting in extensive flooding and damage to infrastructure, with the agricultural sector being particularly hard-hit. 6. Typhoon Gaemi highlighted the need for improved flood management systems and adaptive strategies in the affected regions to mitigate future risks. 7. The event underscored the interconnectedness of geological processes and climatic events, demonstrating how climate change can amplify the impacts of natural disasters. 8. Lessons from Typhoon Gaemi emphasize the importance of early warning systems, community preparedness, international cooperation, and sustainable development practices to enhance resilience. |


