Taxonomy is the science of classifying living organisms into different groups based on their characteristics. The system helps in organizing and naming diverse species for easy identification and study. The term was first coined by Carl Linnaeus, who is known as the father of taxonomy. Understanding taxonomy is vital for researchers, scientists, and students in the field of biology.
- Taxonomy organizes life forms systematically for better study and understanding.
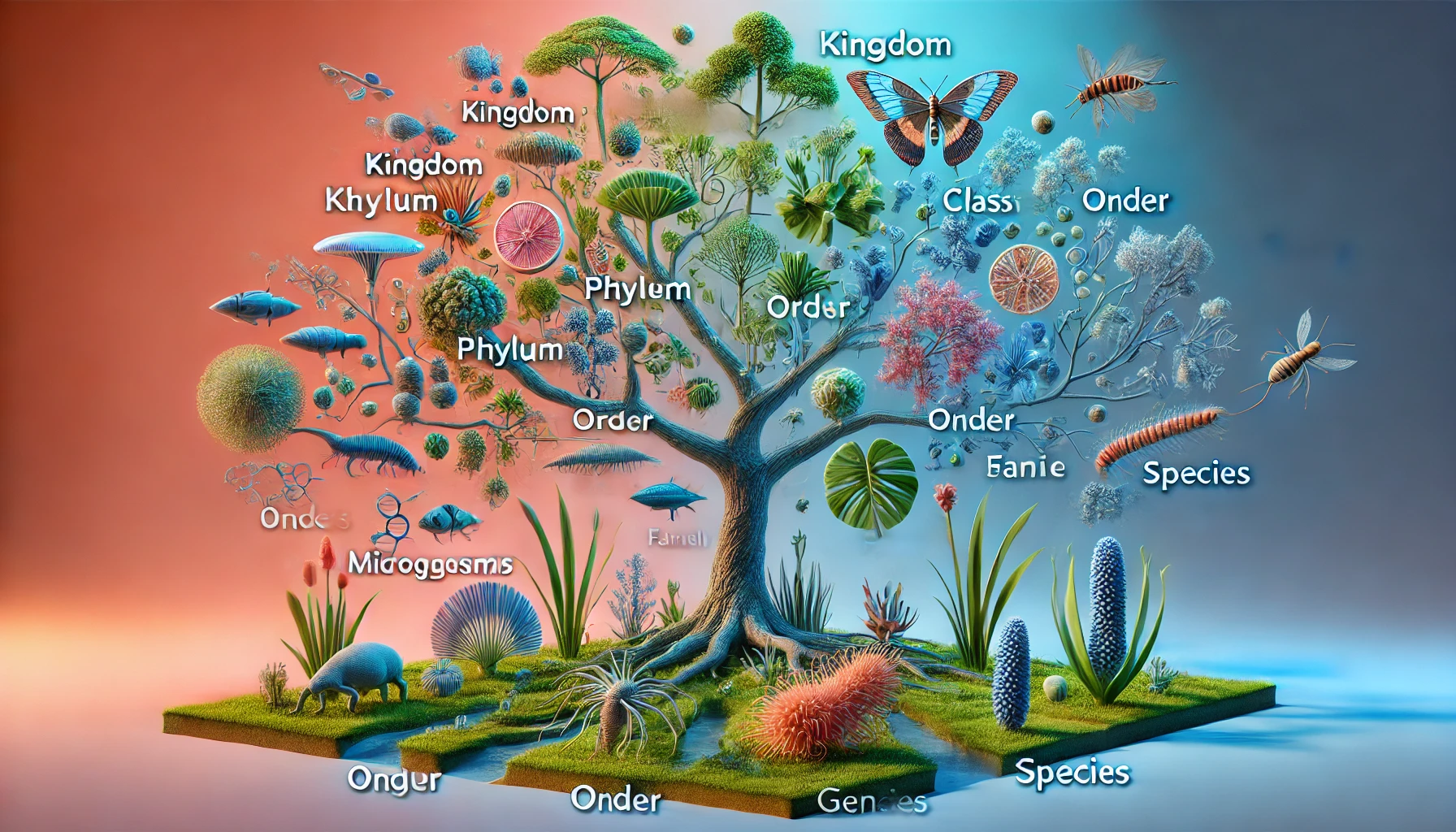
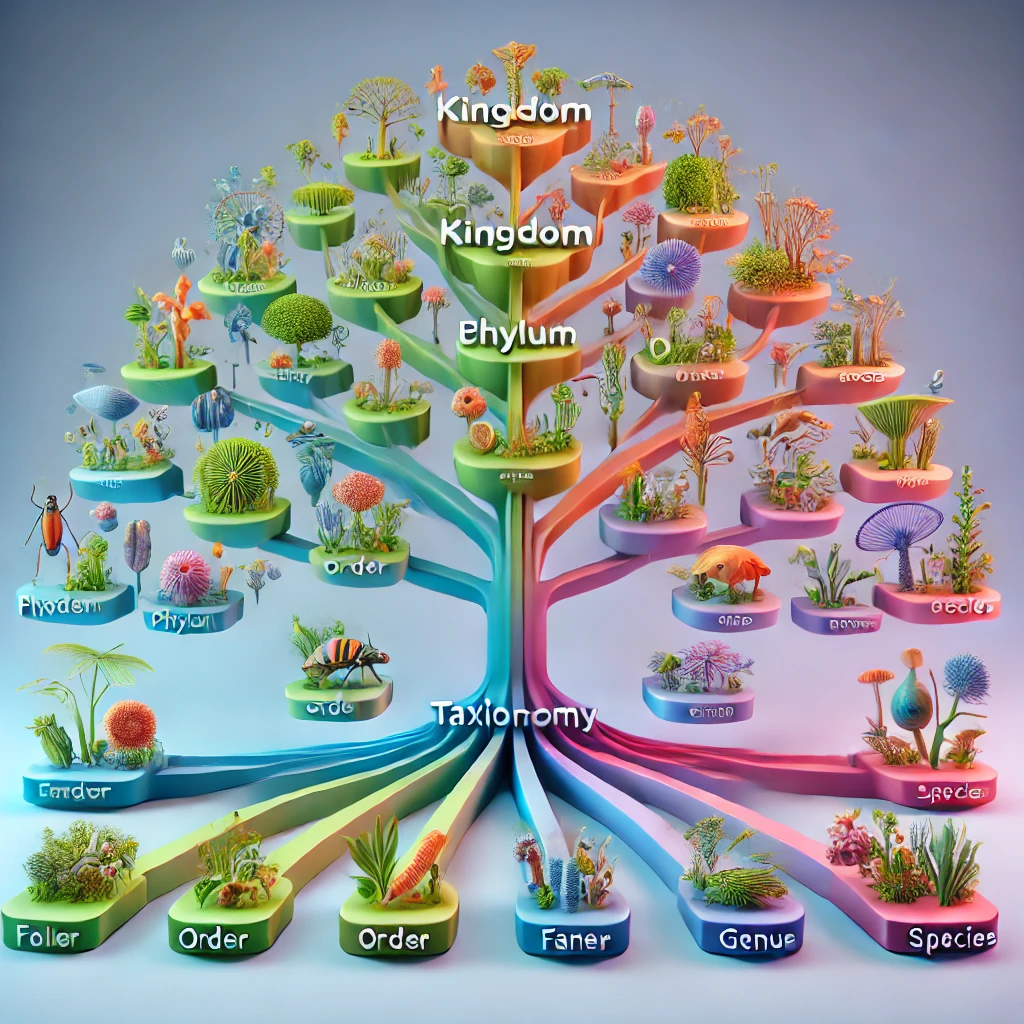
- It categorizes species into hierarchical groups such as kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
- The classification system aids in understanding the relationships between various organisms.
What is taxonomy, and why is it essential? Taxonomy simplifies the complex diversity of life on Earth. It groups similar organisms, making it easier to identify and study them. By classifying plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms into distinct groups, researchers can study their characteristics, evolutionary relationships, and interactions with other organisms. The standardized naming system helps avoid confusion and ensures that scientists across the globe can understand and refer to the same species in a uniform manner.
| GS Paper | General Studies Paper III |
| Topics for UPSC Prelims | Classification, nomenclature, kingdom, phylum, species |
| Topics for UPSC Mains | Importance in biodiversity conservation, Applications in agriculture, medicine, and ecology, Identification of new species, genetic diversity |
Importance of Taxonomy in Biology
Taxonomy plays a crucial role in biology. It provides a universal system for naming and categorizing species. The structure helps in communication, research, and the conservation of biodiversity. Without a standardized classification, studying the vast number of organisms on Earth would be chaotic and inefficient.
In addition, taxonomy allows scientists to understand the evolutionary history of species. By identifying similarities and differences between organisms, they can trace their origins and evolutionary paths. This, in turn, aids in studying the process of evolution and adaptation in different environments.

Carl Linnaeus – The Father of Taxonomy
Carl Linnaeus, the father of taxonomy, developed the binomial nomenclature system in the 18th century. This method assigns each species a unique scientific name composed of two parts: genus and species. For example, the scientific name of humans is Homo sapiens. Linnaeus’s system brought order to the chaotic naming of species and is still used today with some modifications. His work laid the foundation for modern taxonomy, enabling a standardized approach to naming and classifying living organisms.
How Does Taxonomy Categorize Species into Hierarchical Groups?
Taxonomy categorizes living organisms into a hierarchy of groups based on shared characteristics. This hierarchical classification is broken down into several levels, starting with the broadest group and narrowing down to the most specific. The primary levels include:
- Kingdom: The largest and most general category. For instance, animals belong to the kingdom Animalia, while plants belong to Plantae. This level helps classify organisms into major groups based on basic characteristics.
- Phylum: This group divides kingdoms into smaller groups based on major body structures or functions. For example, animals with backbones are classified into the phylum Chordata.
- Class: Further divides phyla into groups of organisms that share more specific characteristics. For example, mammals belong to the class Mammalia within the phylum Chordata.
- Order: Breaks down classes into even smaller groups. For instance, mammals are divided into orders such as Carnivora (carnivores) and Primates.
- Family: Groups organisms that have closer similarities than those within an order. For example, the family Felidae includes cats, lions, and tigers.
- Genus: Includes closely related species and represents the first part of an organism’s scientific name. For example, in Homo sapiens, Homo is the genus.
- Species: The most specific classification, referring to individual organisms that can interbreed. It forms the second part of the scientific name, such as sapiens in Homo sapiens.
This hierarchical system provides a framework that helps biologists study, identify, and understand the intricate relationships between various forms of life.
Applications of Taxonomy in Various Fields
Taxonomy has far-reaching applications beyond scientific research. It plays a significant role in fields like medicine, agriculture, conservation, and environmental science:
- Medicine: Identifying pathogens accurately is crucial for developing vaccines and treatments. Taxonomy helps in classifying bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms to understand diseases better.
- Agriculture: Classifying crops and pests enables the development of pest-resistant varieties, ensuring food security. Knowledge of plant taxonomy aids in breeding and biotechnology research.
- Conservation: Recognizing and categorizing endangered species is essential for their protection. Taxonomy helps in assessing biodiversity, guiding conservation efforts.
- Environmental Science: Understanding ecosystems requires knowledge of the relationships between various species within them. Taxonomy aids in studying and managing ecosystems effectively.
Challenges in Taxonomy
Despite its importance, taxonomy faces challenges. The discovery of new species and the need for accurate classification demand constant updates to the taxonomic system. With millions of species still unidentified, taxonomists are continually working to catalog the world’s biodiversity. Additionally, scientific advancements and changes in understanding species’ evolutionary relationships can lead to reclassification, adding complexity to the system.
Conclusion
Taxonomy is the backbone of biological sciences, offering a structured way to categorize and study the immense diversity of life. It helps in understanding the relationships, origins, and evolution of species. By organizing species systematically, it enhances communication and research in biology and other related fields. The work of Carl Linnaeus, the father of taxonomy, continues to influence modern classification, proving its enduring value. Understanding what is taxonomy and its significance equips us to better explore and conserve the natural world.
| Taxonomy UPSC Notes |
| 1. Taxonomy is the science of classifying living organisms based on their characteristics to organize and study them systematically. 2. It categorizes life forms into a hierarchical system: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. 3. The binomial nomenclature, developed by Carl Linnaeus (the father of taxonomy), assigns each species a unique scientific name. 4. Taxonomy provides a universal system for naming species, aiding in communication, research, and conservation of biodiversity. 5. Modern taxonomy incorporates genetic analysis to identify evolutionary relationships, leading to more accurate classifications. 6. It plays a crucial role in fields like medicine, agriculture, conservation, and environmental science by organizing species for effective study. |