Photosynthesis is the process of converting light energy into chemical energy by plants. First, light energy produces glucose form of sugar that gives the plant the energy it needs. If it weren’t for photosynthesis, there would be no life on Earth because plants are the base of the food cycle. Not only is this process important to plants but also to any living organism that is dependent on the plants for food and air. Plants and other organisms, such as algae and cyanobacteria, have the unique ability to perform photosynthesis. This occurs in specialized structures within cells. Where does photosynthesis take place? It takes place in the chloroplasts, which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll that absorbs light.
- Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight, and the photosynthesis process begins.
- Water and carbon dioxide are the raw materials employed.
- Oxygen is released as a by-product.
- Glucose is formed, and that glucose is used for the growth of plants.
| GS Paper | GS Paper III |
| Topics for UPSC Prelims | Basics of Photosynthesis, Chlorophyll and its role in Photosynthesis, Light-dependent and Light-independent reactions, Factors affecting Photosynthesis |
| Topics for UPSC Mains | Importance of Photosynthesis in the Carbon Cycle and Global Warming, Application of Photosynthesis Knowledge in Agriculture and Forestry, Role of Photosynthesis in Climate Change Mitigation |
Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?
Photosynthesis mainly takes place in leaves. The chloroplasts are located in high concentrations in the plant leaf cells. Inside the chloroplasts, the chlorophyll captures sunlight and converts it into energy. It requires light water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose. Even though it mainly takes place in leaves, stems and other components of the plants also contribute mainly when chloroplasts occur.
Steps of Photosynthesis in Plants
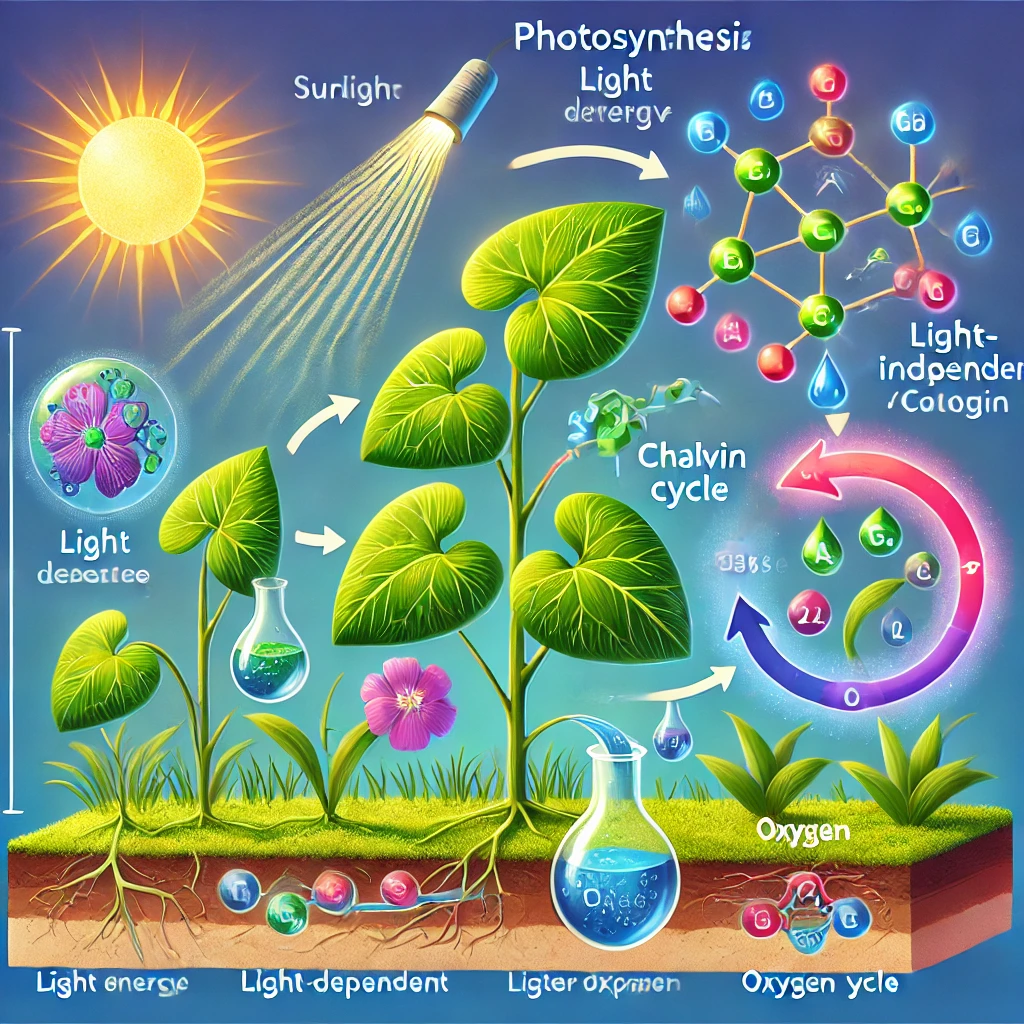
The two phases of photosynthesis are the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
Light-dependent Reactions
Thylakoid membranes, the first step of photosynthesis in plants, use light-dependent reactions. The significance of these reactions is to maintain sunlight and convert it into a chemical energy-a process that produces ATP and NADPH and gives off oxygen as a byproduct.
Light-independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
This is the process whereby carbon dioxide is converted into glucose. This normally takes place in the stroma. This is the fluid-filled region within the chloroplast. The plant stores this glucose to be used as energy during growth, or it can be stored for later use. These two steps thus ensure that plants deliver the effective production of energy needed to allow the plant to grow and thrive.

Factors Controlling Photosynthesis
Many factors can affect the rate and efficiency of it. Factors controlling it include:
- Light Intensity: The greater the intensity of light, the more increased the rate of it.
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration: There must be ample carbon dioxide available to produce optimum glucose.
- Water Availability: There should be ample water because it is required for the splitting up of molecules in the process of light dependent reaction.
- Temperature: Low temperature and high temperature hinder the process
- Chlorophyll Content: In healthy leaves, with abundant chlorophyll content, the activity of photosynthesis is more.
Other forms of photosynthesis
Besides those typical light-dependent and light-independent reactions, there are other it forms – C4 and CAM pathways, which enable plants to capture CO2 effectively and use energy efficiently under the most diverse conditions.
Photosynthesis Type 4
It encompasses alternative pathways like C4 and CAM, which enable plants to adapt to challenging environments. These processes optimize carbon fixation and water usage, ensuring efficient energy production and growth under conditions of high light intensity and limited water availability.
CAM Photosynthesis
CAM or Crassulacean Acid Metabolism is one of those adaptations in specific plants where carbon dioxide fixation takes place at night. This aids in water absorption and allows such plants to grow and survive, therefore flourishing in fundamentally arid lands. It is a special type of it.
Importance of Photosynthesis
Importance of it Importance extends beyond the prosperity of plants. Without the presence of it, there would be no existence of food, neither oxygen and inhospitability for life on this planet. Life on Earth can’t occur if it did not exist since it:
Life Cycle on Earth: Producing Oxygen for Survival
Photosynthesis is the process of life because it favors survival with oxygen. The process by which sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen is absorbed by plants, algae, and bacteria, providing the energy basis for all ecosystems.
Role in the Carbon Cycle
This process is crucial in the global carbon cycle, where it converts carbon dioxide through it into organic compounds. This decreases carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere and, therefore, balances Earth’s temperature by reducing greenhouse gas effects in the fight against climate change.
Origin of Energy to Life
Photosynthesis is the principal energy producer for most kinds of life on Earth. In it, plants manufacture glucose; this glucose acts as a source of energy for plants and is the base of food chains. Herbivores consume plants, while carnivores consume herbivores, thereby converting energy across the ecosystem.
Promotes Agricultural Productivity
Photosynthesis influences crop yields and plant growth, thus enhancing agricultural productivity. The mechanisms of it help scientists and farmers increase food production, develop sustainable agricultural methods and cultivate crops that are more resilient to changing environmental conditions, thereby ensuring food security for an increasingly global population.
Formation of Fossil Fuels
Photosynthesis is one of the processes that contribute to the formation of fossil fuels. These are ancient deposits of carbon-based energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which must have formed after millions of years from dead plant material initially capturing sunlight energy through it. It indeed forms a significant part of modern energy consumption.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is a pretty powerful and complicated process on which life on Earth depends. Knowing where it occurs, the steps of it in plants, and what controls it gives us an understanding of nature’s stunning efficiency. The existence of other types of it emphasizes how versatile the plant species is in climate.
| Photosynthesis UPSC Notes |
| 1. Photosynthesis is the process where plants convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen. 2. The process primarily occurs in the chloroplasts of plant leaves, where chlorophyll captures sunlight for energy conversion. 3. Photosynthesis involves two stages: light-dependent reactions, where oxygen is released, and the Calvin cycle, where glucose is formed. 4. Light intensity, carbon dioxide levels, water availability, and temperature are key factors regulating the rate of photosynthesis. 5. Some plants use C4 or CAM photosynthesis, adaptations that help them survive in hot, dry environments. 6. Photosynthesis is essential for oxygen production, carbon dioxide absorption, and is the foundation of the global food chain. |



