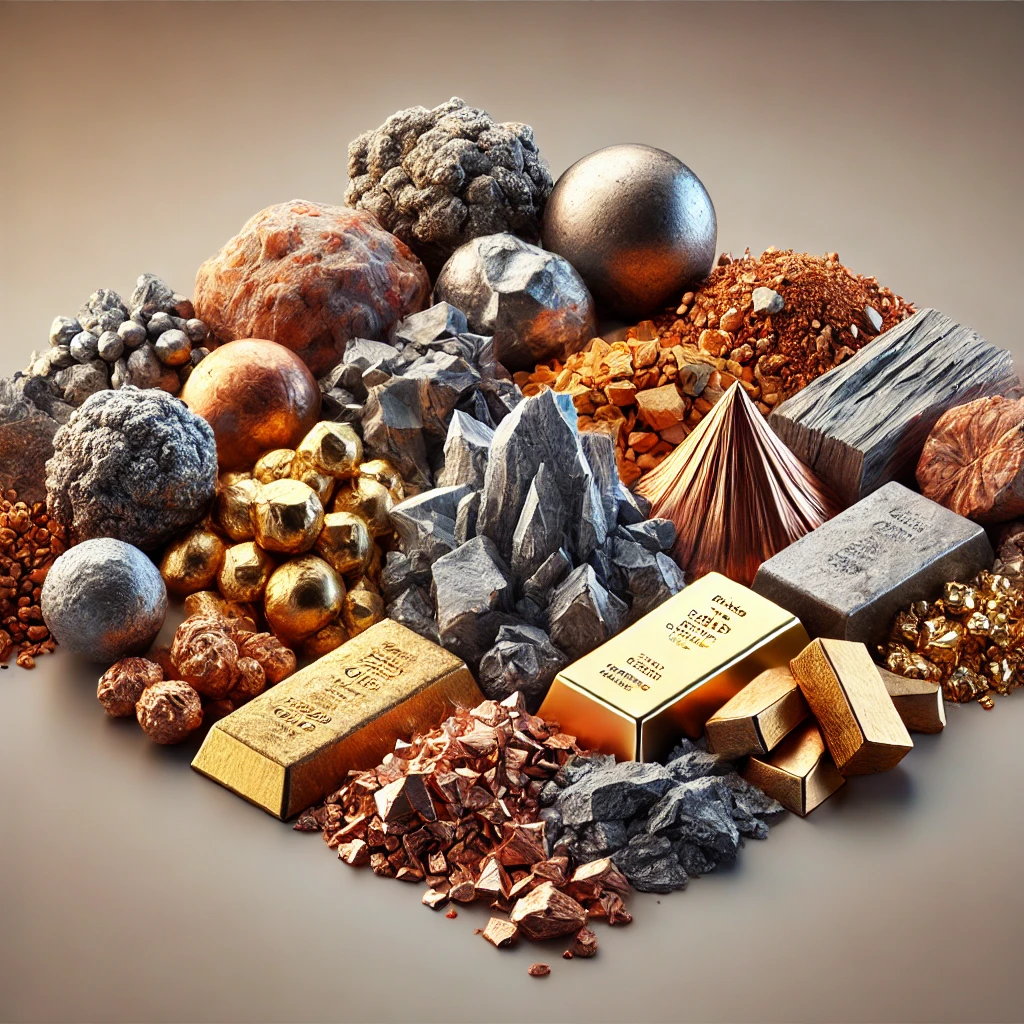
Metallic minerals and non-metallic minerals are essential resources that play a significant role in our daily lives. These minerals are extracted from the Earth and are used in various industries, from construction to technology. Metallic mineral are those that contain metal elements in their chemical composition. They have high economic value and are used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction. Non-metallic mineral, on the other hand, do not contain metal elements. They are used in industries such as ceramics, fertilizers, and building materials.
- Metallic mineral have a shiny appearance and are often dense.
- Non-metallic mineral have a dull appearance and are less dense.
- Metallic mineral are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Non-metallic mineral are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
What are Metallic Minerals?
They are naturally occurring substances found in the Earth’s crust. They contain metal elements that can be extracted through mining and refining processes. These metals are essential for various industrial applications due to their properties like strength, malleability, and conductivity.
Types of Metallic Minerals
Types of Metallic Mineral include ferrous mineral and non-ferrous mineral.
Ferrous Minerals:
- Contain iron as a major component.
- Examples include hematite, magnetite, and pyrite.
- Used in steel production and construction.
Non-Ferrous Minerals:
- Do not contain iron.
- Examples include copper, aluminum, zinc, and lead.
- Used in electrical wiring, aircraft manufacturing, and packaging.
Precious Metals:
- Rare and valuable metals.
- Examples include gold, silver, and platinum.
- Used in jewelry, electronics, and as investments.
Base Metals
- Common metals with high industrial use.
- Examples include nickel, tin, and copper.
- Used in construction, electronics, and machinery.
What are Non-Metallic Minerals?
They are those that do not have metallic elements in their chemical structure. These mineral are essential for industries that require materials with specific non-metallic properties like insulation, heat resistance, and chemical stability.
Types of Non-Metallic Minerals
Non-metallic mineral vary widely, including industrial mineral, precious stones, fertilizer minerals, energy mineral, and chemical mineral.
Industrial Minerals
- Used in manufacturing and construction.
- Examples include limestone, gypsum, and clay.
- Essential for making cement, plaster, and ceramics.
Precious Stones
- Rare and valuable minerals are used in jewelry.
- Examples include diamonds, sapphires, and rubies.
- Valued for their beauty and durability.
Fertilizer Minerals
- Used to enhance soil fertility in agriculture.
- Examples include phosphate rock, potash, and sulfur.
- Crucial for producing fertilizers to support crop growth.
Energy Minerals:
- Non-metallic mineral are used as fuel.
- Examples include coal and uranium.
- Used for generating electricity and as energy sources.
Chemical Minerals
- Used in various chemical processes and products.
- Examples include salt (halite) and fluorite.
- Important for producing chemicals, detergents, and other products.
Difference Between Metallic Minerals And Non-Metallic Minerals
Conclusion
Metallic mineral and non-metallic mineral are essential to the functioning of modern society. Understanding their differences and applications helps in making informed decisions about their use and conservation. As the global demand for these resources continues to grow, it is vital to adopt sustainable practices that protect the environment and ensure the availability of these critical resources for future generations.
| Metallic Minerals UPSC Notes |
| 1. Metallic minerals are primarily used in industries due to their metallic properties, such as conductivity, malleability, and luster. 2. India has rich reserves of metallic minerals like iron ore, bauxite, copper, gold, and manganese. 3. Iron ore is the most significant metallic mineral produced in India, crucial for the steel industry. 4. Bauxite is the primary source of aluminum, found abundantly in states like Odisha, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh. 5. The extraction and processing of metallic minerals contribute significantly to India’s economy but also pose environmental challenges. 6. The distribution of metallic minerals in India is uneven, with specific regions being mineral-rich while others lack these resources. 7. Government policies and initiatives aim to boost the exploration and sustainable extraction of metallic minerals. 8. The mining sector faces challenges such as illegal mining, environmental degradation, and the need for technological advancements in extraction processes. |