Lipids are one of the most essential biomolecules present in every living organism. They perform a remarkable function in most biological processes. These include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Unlike carbohydrates and proteins, lipids do not dissolve in water hence making them unique. They make up the main store of body energy and are needed in the proper cell structure.
- Lipids can be a source of energy; they insulate the body.
- It comprises parts to make the cell membrane; thus, with its assistance, structural integrity is maintained.
- They aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
- Some lipids are hormones while others are precursors of hormones.
- From storing energy to cell signaling, lipids play a very significant role. Knowing what they do can enlighten why they are a vital element in biological activities.
There are many types of lipids, each with unique characteristics. They form an important element of health because they play a wide range of functions in the body.
| GS Paper | General Studies Paper III |
| Topics for UPSC Prelims | Basic structure of lipids, Types |
| Topics for UPSC Mains | Functions in the human body, Role in metabolism and health, Importance in agriculture and industry (e.g., oils, biofuels) |
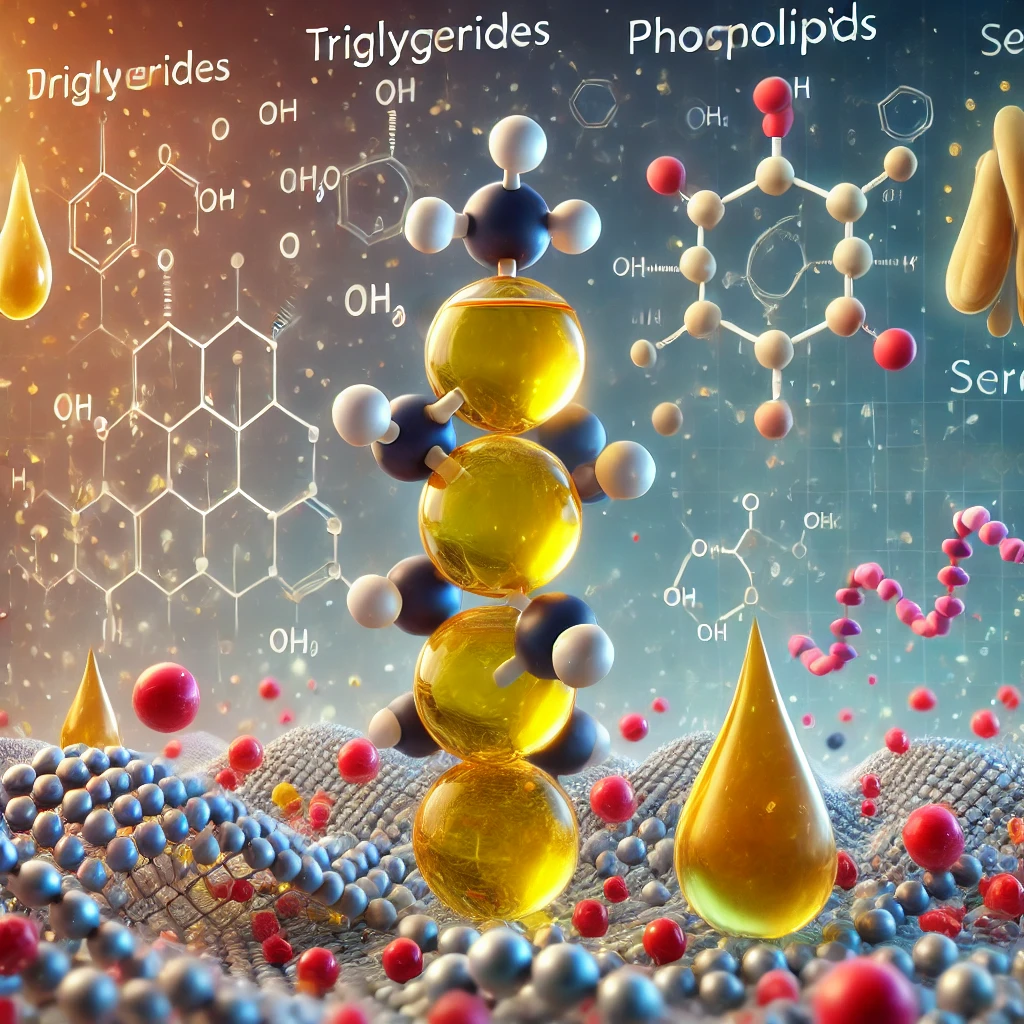
Types of Lipids
Lipids come in different forms, and each performs a different role. These are the main types of lipids:
Triglycerides (Fats and Oils)
These are the most common type of lipids in food and in the body. They consist of three fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol backbone. Triglycerides form considerable energy reserves stored in fat cells. These break down upon demand for the body’s energy to release fuel.
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are an important component of the cell membranes. They also form a bilayer, cutting off the internal environment of the cell from the external one. With this structure, cells are able to maintain a controlled internal environment as well as allow substances into or out of the cell. A classic example of the phospholipid is lecithin, which has a significant role in metabolism of fats.
Steroids
Steroids are a special class of lipids consisting of a four-ring carbon structure. Perhaps one of the most familiar steroids is cholesterol, the more important it is in the formation of cell membranes and hormone synthesis, including sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone. Though as negatively profiled as cholesterol has been, it, too, performs an important function in the body.
Waxes
Waxes are lipids whose chains of fatty acids are bonded to alcohol. They provide protective coverings for plants and animals. For example, the wax that covers the leaves prevents water loss, and the wax of the ear protects the ear canal from dust and microorganisms.
Role of Lipids in the Body
Lipids play many important roles in health and body functions. Here are some of the crucial functions:
Energy Storage and Supply
Energy storage is one of the most fundamental roles of lipids. Extra calorie consumption will be used by converting it into triglycerides stored within cells that contain them. These lipids will be broken down whenever the body lacks them to provide energy. This way, the body will be guaranteed of having sufficient energy for the duration of the periods during fasting or any of the most rigorous body activities.
Insulation and Protection
Lipids acts as insulators, an extra layer of fat under the skin keeps the body temperature warm. It can be an insulator without the proper disbursement and die when it dies off. They can safeguard vital organs because they tend to create padding inside the body, thus having a minimized likelihood to be injured by physical effects on parts of the body.
Structural Components
Primarily, cell membranes are made up of lipids, which are mostly phospholipids. This bilayer structure of lipids provides essential protection for the cell while controlling the movement of substances within and outside the cell. Cells would break down and would not function if they did not contain lipids.
Hormone Production
There exist some lipids that act as precursors in the synthesis of hormones. For example, cholesterol is a vital lipid that participates in hormone synthesis: it can be converted into different hormones, such as cortisol, estrogen, and testosterone. These hormones regulate various physiological activities, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
Food Sources of Lipids
A healthy diet needs to contain lipids to provide adequate essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins to the body. Here are some examples of food sources that are high in lipids:
- Oils: Olive, coconut, and sunflower oil contain fatty acids.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseed, and chia seed contain essential fatty acids
- Avocados: These are rich in monounsaturated fats, which are a means of controlling heart diseases.
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, and tuna are wonderful sources of omega-3 fatty acid
- Dairy products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt have saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Healthy vs. Unhealthy Lipids
Not all lipids are healthy. Healthy fats should be distinguished from unhealthy fats:
Healthy Fats
Unsaturated fats include monounsaturated and polyunsaturated. They reduce bad cholesterol levels. They also lower heart disease risk. Healthy fats are present in olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Unhealthy Fats
Unhealthy fats: Saturated and trans fats contribute to unhealthy fats. Saturated fats are found in animal products, including butter, cheese, and red meat. Consumption above a certain level is associated with the rise of bad cholesterol and increased risk of heart disease. Trans fats, mainly found in processed and fried foods, are particularly unhealthy and should be limited in the diet.
Importance of Lipid Balance in Diet
To achieve general wellness, balance in lipids within one’s diet must be maintained. Although some fats within the human body are essential to proper bodily functions, excessive intakes of unhealthy fats contribute to numerous health problems. High consumption of saturated and trans fats can allegedly raise cholesterol levels, resulting in heart disease, stroke, or becoming an obese individual.
On the other hand, a diet rich in healthy fats has benefits to the brain, reduces inflammation, and is also good for maintaining heart health. All these additions include unsaturated fat sources such as nuts, seeds, and fish.
Lipid and Disease Prevention
In the right quantity and quality, a chunk of lipids would play a pretty well and bright role in preventing diseases. They help prevent chronic diseases, such as coronary heart disease and arthritis, as well as some types of cancers, to name a few. Phospholipids are conducive to brain health because they aid in the development of cell membranes within the nervous system.
Conclusion
Lipids are another very important biomolecule in the body. They can store energy, keep up cell structure and hormone production, as well as protect certain organs. The appropriate types of lipids should be taken within the diet for general health. Although these fats are to be sufficiently consumed within the diet, harmful fats must also be avoided too. Being knowledgeable about the different functions, types, and dietary sources of lipids teaches people how they can strategically decide on what to eat, hence keeping them in a good position for a balanced healthy lifestyle.
| Lipids UPSC Notes |
| 1. Lipids are biomolecules that store energy, provide insulation, and form cell membranes. They include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. 2. Triglycerides, the most common lipids, have three fatty acids attached to glycerol. They serve as the body’s energy reserve. 3. Phospholipids are crucial for cell membrane structure, helping maintain the internal environment of cells and allowing substance movement. 4. Steroids, like cholesterol, are involved in hormone production, cell membrane formation, and regulating various physiological processes. 5. Healthy fats (unsaturated) lower bad cholesterol, reducing heart disease risk, while unhealthy fats (saturated and trans) increase health risks. 6. A balanced intake of lipids is essential, with omega-3 fatty acids reducing inflammation and supporting brain and heart health. |