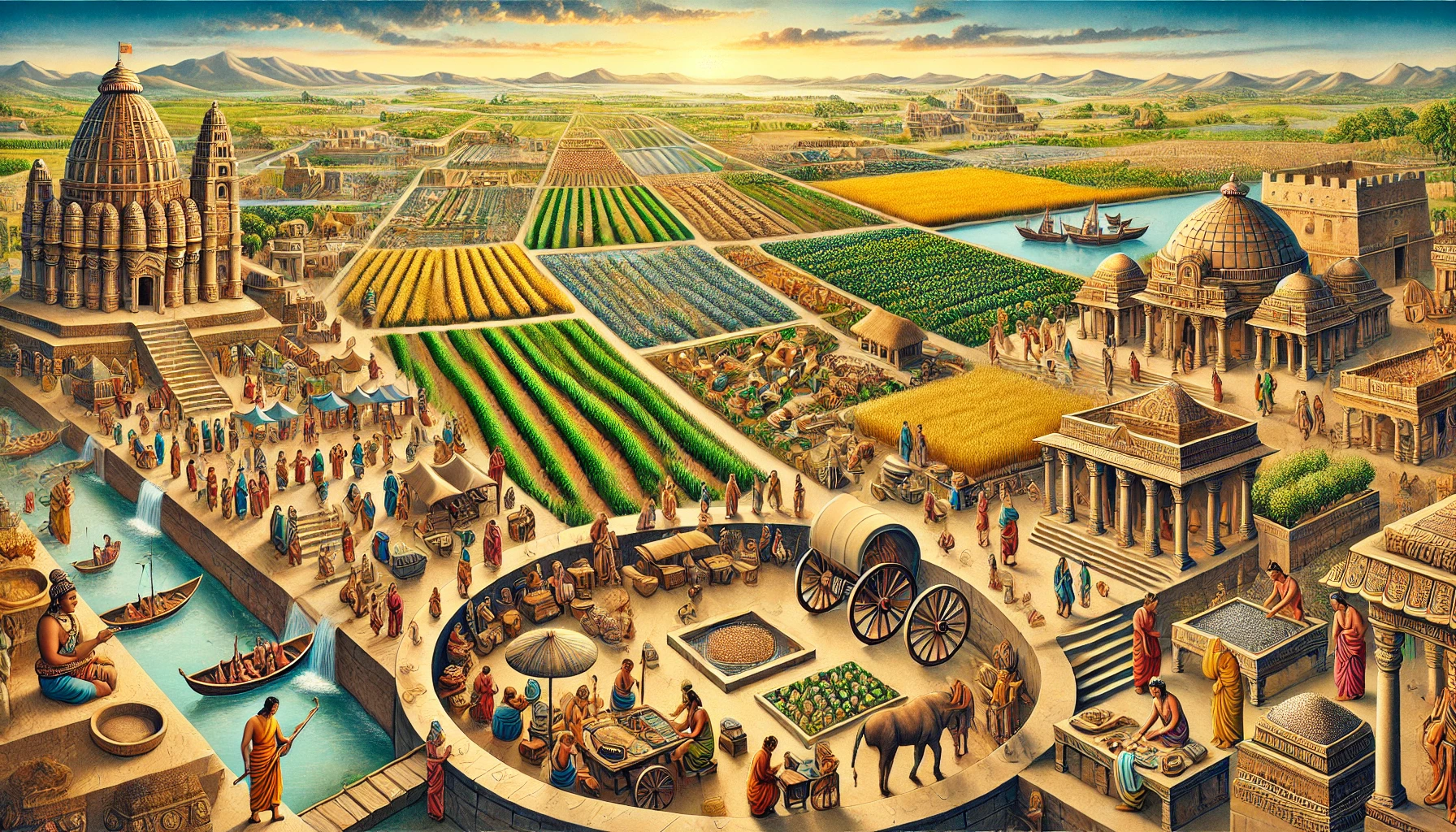

The Gupta Economy was a period of economic prosperity and growth. It was marked by advancements in agriculture, trade, crafts, and guilds. Many historians often consider the economy of Gupta period as one of the golden ages of ancient India, where stability and wealth prevailed across the empire. The Gupta Empire economy was diverse, encompassing various sectors that contributed significantly to the overall prosperity of the region.
Agriculture was the primary occupation during the Gupta Empire. The fertile plains of the Ganges and other rivers made farming highly productive. The Gupta Economy relied heavily on the cultivation of staple crops like rice, wheat, and barley. These crops not only supported the local population but also allowed for surplus production, which could be traded. The system of land revenue collection was efficient, contributing to the empire’s wealth. Farmers paid taxes either in kind or in cash, depending on the region and crop yield.
| GS Paper | General Studies Paper I |
| Topics for UPSC Prelims | Role of guilds in the economic structure of the Gupta period, Major trade routes and commodities |
| Topics for UPSC Mains | Role of guilds in the economic structure of the Gupta period, Major trade routes, and commodities |
The Gupta Empire economy and trade were highly developed, with both domestic and international trade routes being extensively utilized. The period saw the rise of trading hubs, with cities like Pataliputra and Ujjain becoming significant centers of commerce. Internal trade connected various parts of the empire, while external trade extended to regions like Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean.
Merchants played a crucial role in the Gupta Economy, moving goods across vast distances. The trade items included textiles, spices, precious stones, and metals. The Gupta Empire economy benefited from the export of silk, which was in high demand in foreign markets. In return, the empire imported luxury items like ivory, horses, and wines. The state effectively protected trade routes, guaranteeing the safety of merchants and maintaining a smooth flow of goods.
Crafts were an essential part of the Gupta Economy, with artisans producing a wide range of goods, from pottery to textiles. The period witnessed the flourishing of various crafts, supported by the establishment of guilds. These guilds were organizations of craftsmen and merchants, that regulated trade practices, ensured quality, and protected the interests of their members.
The economy of Gupta period was significantly influenced by these guilds, which often acted like banks, lending money to their members and even to the state. The existence of such guilds indicates a high level of organization and economic maturity within the empire. Crafts produced during this time were of high quality and were in demand both within and outside the empire.
The Gupta Empire efficiently administered its economy, implementing a strong revenue system that met the state’s requirements. The empire relied primarily on land revenue as its main source of income. The state collected a portion of agricultural produce as tax. It was then allocated towards funding public works, sustaining the military, and backing the royal court. The efficiency of this system was a key factor in the empire’s prosperity.
To some extent, local officials were responsible for decentralizing the administration by collecting revenue and maintaining law and order. The approach allowed for better resource management and ensured close monitoring and regulation of the empire’s economic activities.
The Gupta Economy was a complex and well-organized system that contributed to the golden age of the Gupta Empire. Agriculture, trade, crafts, and guilds formed the backbone of this economy, ensuring prosperity and stability throughout the empire. The economy of Gupta period supported a flourishing society. It left a lasting legacy that influenced subsequent economic systems in the region. The Gupta Empire economy and trade were remarkable for their time, setting a benchmark for future empires in India.
| Gupta Economy UPSC Notes |
| 1. The Gupta Economy was marked by agricultural prosperity, with fertile plains supporting the cultivation of rice, wheat, and barley, leading to surplus production. 2. Trade flourished both internally and externally, with cities like Pataliputra and Ujjain becoming significant commercial hubs, connecting the empire to Southeast Asia and the Mediterranean. 3. Crafts and guilds played a crucial role, with artisans producing high-quality goods, supported by guilds that regulated trade practices and acted as financial institutions. 4. The revenue system was well-organized, with land revenue as the primary source of income, funding public works, the military, and the royal court, ensuring economic stability. 5. Guilds not only regulated the quality of crafts but also lent money to members and the state, showcasing the economic maturity of the Gupta Empire. 6. The decentralized administration allowed local officials to effectively manage resources and maintain order, contributing to the overall prosperity and stability of the Gupta economy. |
Minilateralism is transforming the global diplomacy as it introduces smaller, targeted partnerships in order to…
India’s GDP Growth Forecast Revised Downwards by RBI The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on…
India is losing its opportunities to sustain agriculture due to severe soil degradation. Recent studies…
India’s Economic Growth Outlook Revised The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has brought down India's…
Startup Ecosystem in India has emerged as a global leader, with over 140,000 recognized startups…
India’s GDP Growth Forecast Revised by RBI The Reserve Bank of India had trimmed its…