Climate change, in simple terms, is a case of record change in general trends of temperature and weather conditions over a considerable period. While natural variability exists, the cause that involves humans emitting gases into the atmosphere is the cause. Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide and methane, have been major factors in accelerated climate change since the era of industrialization. These changes include rising global average air and ocean temperatures, widespread melting of snow and ice, and rising global average sea levels.
- According to the National Intelligence Council, by 2025 unprecedented economic growth, coupled with 1.5 billion more people, will put pressure on the world’s resources—particularly energy, food, and water—raising the specter of scarcity emerging as demand outstrips supply.
- The most immediate effects of global climate change are likely to be strongly felt in the poorest countries with relatively weaker governance structures, especially in Africa and Asia.

Impact on National Security
Climate change is increasingly recognized as a ‘threat multiplier’ that exacerbates existing risks and creates new security challenges. Here are key ways in which climate change impacts national security:
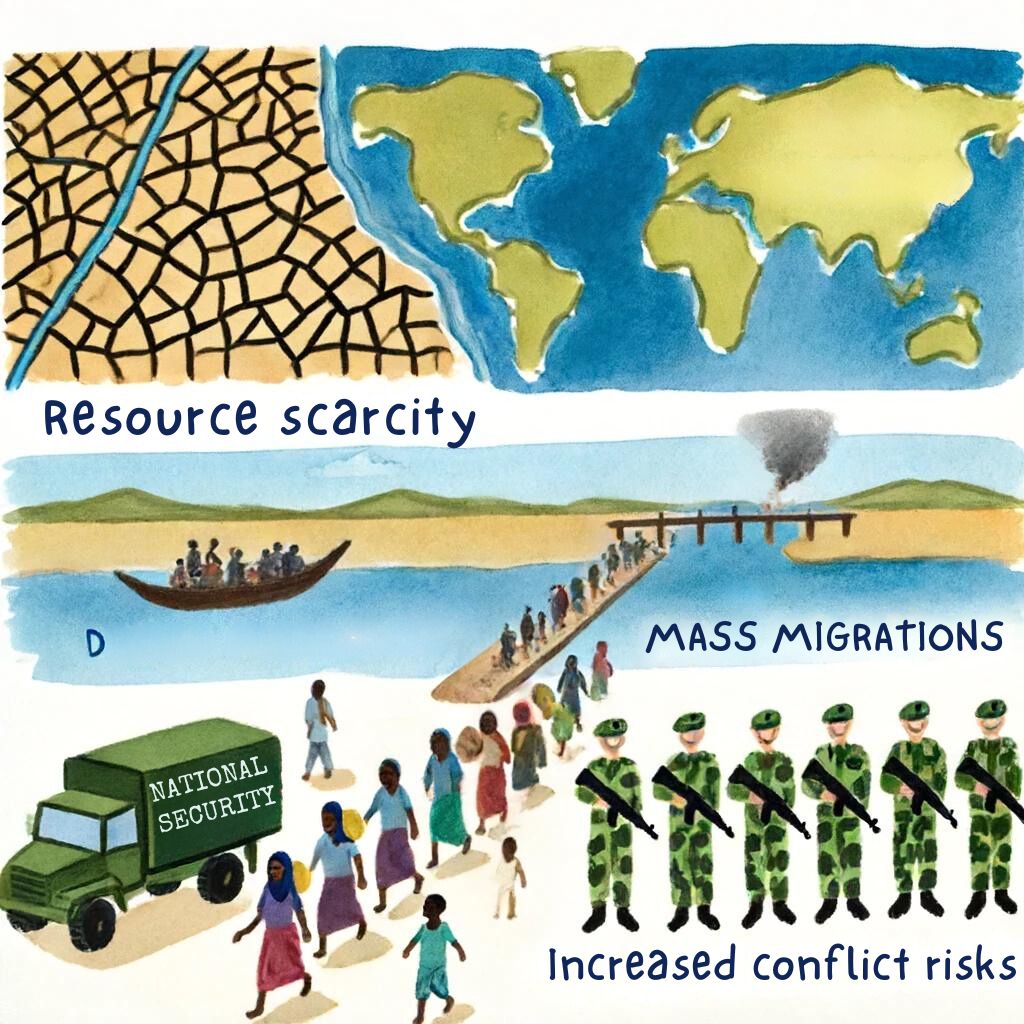
- Resource Scarcity: Changes in water availability and agricultural productivity due to climate change will lead to food and water scarcity. Such scarcity may spark the ignition of competition among local communities, states, and even nations.
- Mass Migrations: Increased sea levels and severe events, such as hurricanes and droughts, will force mass migrations of people, which, again, increases overcrowding in certain areas. This threatens to stress local resources and infrastructure, fuelling possible social strife and communal violence.
- Increased Risk of Conflict: Resource competition and mass migrations all combine to create the potential for increased tensions and conflict. For example, resource scarcity has already heightened tensions over water supplies in areas such as the Middle East.
Case Studies
Several case studies highlight the impact of climate change on global security.
- Syria: The severe drought in Syria from 2006 to 2009 was worsened by a long-term trend of increasing temperatures and decreasing rainfall linked to climate change. Thus contributing to social unrest and the eventual civil war.
- Lake Chad Basin: Climate change has contributed to the shrinking of Lake Chad, leading to economic hardships and contributing to the rise of terrorist groups like Boko Haram. It capitalizes on the increasing local discontent and economic instability.
International Responses
To mitigate the impacts of climate change on security, several international efforts have been undertaken:
- United Nations Security Council: Recognizing the link between climate change and security. The UNSC has held debates on the implications of climate change for world peace and security.
- Global Agreements: Agreements such as the Paris Agreement aim to mitigate climate change by reducing carbon emissions. Nations globally are encouraged to pledge to reduce their carbon footprint to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Future Projections of Climate Change
Scenarios of future situations, based on current climate and security trends, are indicative that climate change will further in the next decades be a serious disrupting factor for world stability. Continued global warming is likely to increase resource scarcity, induce more frequent and intense natural disasters, and sharpen the risks of migration and conflict.
Each of these challenges calls for proactive international cooperation and sound policy frameworks for them to be met effectively. This has made it critical for the integration of consideration of climate in both national and international security strategies in a way that manages risks associated with the change of climate.

Conclusion
The combination of climate change and global security is indeed a crucial point of concern that, until now, has not been stirred up with due attention by global leaders, policymakers, and researchers. Addressing these issues through comprehensive and sustained international efforts is very instrumental in securing a stable and peaceful future.
| Climate Change UPSC Notes |
| 1. Climate change is defined as a general rise in temperature and alteration of weather conditions over a very long period of time, strongly pointedly by activities of human life, which include the emissions of greenhouse gases since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. 2. Major contributors include CO₂ and CH₄, and both have been speeding up climate change by capturing heat in Earth’s atmosphere. 3. Economic growth and increasing populations will result in shortages of vital resources in many parts of the world in 2025. 4. Countries, especially in Africa and Asia, are likely to be more vulnerable to the adverse consequences of climate change owing to weaker governance and infrastructure. 5. Climate change is a ‘threat multiplier’ that amplifies the already existing risks of resource scarcity, migration, and conflict. 6. Competition for basic resources such as water may heighten tensions and lead to conflict-as has been repeatedly witnessed in places such as the Middle East. 7. Global agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, set a target to lessen the impacts of climate change through the reduction of emissions. Climate is now also being integrated into national and international security strategies. |


