India’s Cabinet has approved the BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) proposal to boost manufacturing in the biotechnology sector. While India has made significant strides in areas like vaccine development, the country has yet to fully capitalize on the broader potential of biotechnology. The BioE3 policy focuses on six verticals, including bio-based chemicals, functional foods, precision biotherapeutics, climate-resilient agriculture, carbon capture, and marine/space research. While well-intentioned, the policy’s success depends on long-term financial and infrastructural support from both the central and state governments.
| GS Paper | General Studies III |
| Topics for UPSC Prelims | Biotechnology sector, Vaccine development, Climate-resilient Agriculture, Carbon capture, Biopharmaceuticals, Biotech-KISAN, Union Budget 2023-24, GenomeIndia Project, Diphtheria, Tetanus and Pertussis, Bt cotton, Golden rice, Active pharmaceutical ingredients, Biofuels. |
| Topics for UPSC Mains | Current Status of India’s Biotechnology Sector, Significance of Biotechnology for India, Key Challenges Hindering the Growth of Biotechnology in India. |
Origin of the Article
This editorial is based on “Biotech enigma: On the BioE3 proposal and beyond” which was published in The Hindu on 30/08/2024. The article highlights the recent BioE3 policy as a significant initiative to boost India’s biotechnology sector but emphasizes that its success hinges on sustained financial support and collaboration between central and state governments.
Relevancy for UPSC Students
Understanding the BioE3 policy and the current status of India’s biotechnology sector is crucial for UPSC aspirants. This topic is relevant to GS Paper-2 and GS Paper-3, covering areas like government policies, biotechnology, and economic development. It also helps in understanding the challenges and opportunities in India’s biotech sector, which can be useful for essay writing and interviews.
Why in News
The BioE3 policy is making headlines as it represents a significant leap in India’s biotechnology sector, aiming to bolster economic growth, environmental sustainability, and employment. For UPSC aspirants, understanding this policy is crucial as it links to government initiatives, economic development, and technological advancements—topics frequently covered in GS Papers 2 and 3. Previous UPSC questions on biotechnology and agricultural advancements underscore the importance of this evolving sector.

Current Status of India’s Biotechnology Sector
The country has emerged as an upcoming player in the international biotechnology arena, showing remarkable economic and innovative performance. The section covers an overview of where India is now, the successes and various economic outputs in the international arena of biotechnology.
Status: India figures among the top 12 biotech destinations of the world and is ranked third in the Asia-Pacific region. The country’s Bioeconomy has reached an estimated USD 130 billion in the year 2024, thus playing a full-fledged role in making India a USD 5 trillion economy by 2024. With 3% of the world share in biotechnology, India is fast emerging as a hub for innovative and affordable healthcare solutions.
Biotechnology Categories in India
- Biopharmaceuticals lead in the global supply of low-cost drugs and vaccines. The country is a pioneer in biosimilars, boasting the highest number of domestic market approvals.
- In Bio-Agriculture, India holds the fifth largest area of organic agricultural land globally, with the potential to significantly boost its BioEconomy.
- Bio-industrial biotechnology is transforming manufacturing and waste disposal processes.
- Bio-IT & BioServices thrive due to strong capabilities in contract manufacturing, research, and clinical trials, hosting numerous US FDA-approved plants.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has introduced various measures to promote the biotechnology sector, ensuring sustainable growth and global competitiveness.
- 100% FDI: The government allows 100% FDI under the automatic route for greenfield pharma and medical device manufacturing, providing favorable conditions for brownfield investments.
- National Biotechnology Development Strategy 2021-25: This strategy aims to make India globally competitive in biotechnology, targeting a USD 150 billion Bioeconomy by 2025 through research, innovation, and entrepreneurship.
- Biotech-KISAN: This initiative connects farmers with scientists, promoting sustainable agriculture through 51 Biotech-KISAN hubs, focusing on soil health, irrigation, and new agri-technologies.
- Union Budget 2023-24: The establishment of 500 new ‘waste to wealth’ plants under the GOBARdhan scheme, with an investment of INR 10,000 crore, highlights the government’s commitment to sustainable development.
- GenomeIndia Project: This project aims to sequence and analyze genomes of a representative Indian population, enhancing understanding of genetic diversity for public health improvements.
- First National Biotechnology Development Strategy 2007: Launched by the Department of Biotechnology, this strategy laid the groundwork for India’s biotechnology development.

Significance of Biotechnology for India
Biotechnology holds multifaceted importance for India’s economic growth, health, agriculture, environment, and innovation sectors.
- Economic Powerhouse-Biotech’s Billion-Dollar Promise: The biotechnology sector is poised for explosive growth, potentially reaching USD 150 billion by 2025. Success stories like Biocon demonstrate the global competitiveness of Indian biotech firms, contributing significantly to GDP and job creation.
- Vaccine Prowess: India produces 60% of the world’s vaccines, fulfilling 40-70% of WHO’s demand. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Serum Institute emerged as the world’s largest vaccine manufacturer, enhancing India’s global health influence.
- Agricultural Revolution 2.0: Biotechnology addresses agricultural challenges with solutions like Bt cotton, drought-resistant rice, and golden rice, improving food security and farmer incomes.
- Environmental Safeguard: Biotechnology offers solutions for environmental issues through bioremediation, biodegradable plastics, and carbon capture technologies, aiding in climate action goals.
- Innovation Ecosystem: With over 5,000 biotech startups, innovation hubs like Bangalore Bioinnovation Centre and Genome Valley, and government initiatives like Atal Innovation Mission, India’s biotech sector is fostering a vibrant innovation ecosystem.
- Self-Reliance in Critical Sectors: Biotechnology reduces import dependence through eco-friendly alternatives, biofuels, and domestic production of APIs, enhancing health security and economic resilience.
- Futuristic Frontiers-Marine and Space Biotechnology: Research in marine and space biotechnology opens new frontiers, unlocking biofuels, novel materials, and innovations applicable on Earth.
- Biotech-A Catalyst to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals: Biotechnology contributes to UN SDGs, addressing hunger, health, clean water, clean energy, and climate action, positioning itself as a driver of India’s sustainable future.
Key Challenges Hindering the Growth of Biotechnology in India
Despite its potential, the biotechnology sector in India faces significant obstacles that hinder its growth and innovation.
- Regulatory Maze: The complex regulatory environment slows biotech innovation, with overlapping jurisdictions and cumbersome approval processes for GMOs, exemplified by the moratorium on Bt brinjal.
- Funding Famine: Securing adequate funding is a major hurdle due to long gestation periods and high risks. The biotechnology sector receives only 0.05% of India’s GDP as funding from the Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Infrastructure Inadequacies: India’s biotech infrastructure lags in high-end research equipment, state-of-the-art laboratories, and reliable cold chain infrastructure, crucial for pharmaceutical distribution.
- IP Insecurity: Intellectual property protection remains a concern, with challenges in patent application and enforcement, highlighted by debates over COVID-19 vaccine patents.
- Global Gatecrashing: Indian biotech firms face stiff competition from established global players, requiring significant investments in clinical trials, regulatory compliance, and marketing to compete.
- Talent Tug-of-War: Despite producing many biotech graduates, India faces a shortage of skilled professionals in cutting-edge areas due to brain drain and skills mismatch.
- Ethical Challenges: Ethical and social dilemmas, such as those surrounding GM crops and gene editing, create roadblocks to research and commercialization.
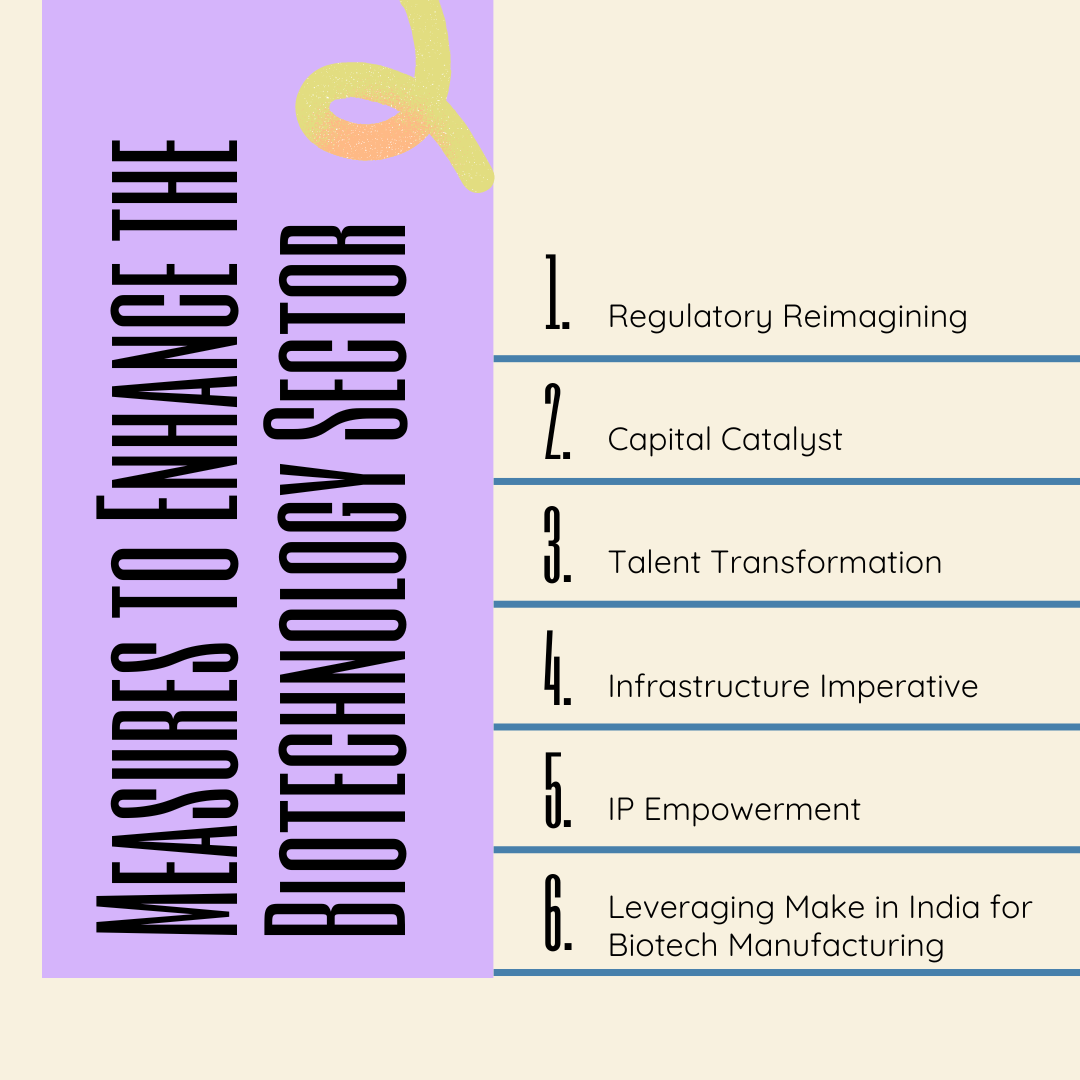
Measures to Enhance the Biotechnology Sector
To overcome challenges and boost the biotechnology sector, India can adopt several potential strategies.
- Regulatory Reimagining: Establish a single-window clearance system for biotech projects by creating a unified Biotechnology Regulatory Authority of India, implementing a risk-based assessment approach for faster approvals.
- Capital Catalyst: Create a dedicated Biotechnology Investment Fund through public-private partnerships, offering grants, soft loans, and equity investments tailored to different development stages.
- Talent Transformation: Launch a National Biotechnology Skill Development Program, focusing on emerging areas, mandating industry internships, and encouraging interdisciplinary education.
- Infrastructure Imperative: Develop a network of shared high-end research facilities and specialized biotech manufacturing zones, investing in cold chain infrastructure.
- IP Empowerment: Strengthen the IPR regime by increasing patent examiners and establishing a Biotech Patent Pool for collaborative research and technology transfer.
- Leveraging Make in India for Biotech Manufacturing: Expand the PLI scheme to cover a wider range of biotechnology products, establishing Biotech Manufacturing Corridors with specialized infrastructure.
PESTEL Analysis
| Political: Biotechnology is encouraged by the Indian government through policies and programs like 100% FDI for greenfield projects, National Biotechnology Development Strategy, and the BioE3 policy. Greater coordination between the centre and the states must be effected. Then, the regulatory reforms involve establishing a single-window clearance system for biotech projects. Economic: Biotechnology is integral to India’s aspiration to become a USD 5 trillion economy by 2024 and achieve potential growth of as much as USD 150 billion by 2025. Significant gaps in funding and strong competition from major global players remain concerns. The expansion of the PLI scheme and creation of a Biotechnology Investment Fund are expected to provide the needed economic stimulus. Social: Biotechnology holds tremendous promise for significant social dividends, from jobs requiring high skills to healthcare. However, ethical considerations and social acceptance of selected biotech applications could act to influence citizen support, and thus the rates of adoption. Technology: It has emerged as a hub for biopharmaceuticals, agricultural biotech, and bio-services, with more than 5,000 startups working on innovative ideas. This, however, is inhibited by deficits in physical infrastructure and a lack of talent in advanced biotech areas, thus creating an urgent requirement for serious investment in research facilities and in a National Biotechnology Skill Development Program. Environmental: These environmental factors come through innovations in climate-resilient agriculture, waste management, and biodegradable materials. Carbon capture and functional foods are also manifestations that the sector has the ability to reduce environmental impacts. Legal: Complex regulatory structures reduce the rate of approval of biotech innovations. Strengthening the IP regime and providing a Biotech Patent Pool could improve legal protection and be a spur to innovation. |
Conclusion
The BioE3 initiative represents a significant step towards harnessing India’s biotechnology potential. For its success, robust financial and infrastructural support is crucial. This initiative could drive economic growth, enhance environmental sustainability, and create employment, but it requires effective collaboration between central and state governments to overcome existing challenges. India’s continued progress in biotechnology will be pivotal for its global standing and sustainable development goals.
| UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs) Mains Q. Discuss the potential of biotechnology in addressing global environmental challenges like climate change, carbon capture, and sustainable agriculture. How can India leverage its biotechnology sector to become a global leader in these fields? (GS Paper III, 2022) Q. Discuss the importance of the GenomeIndia Project in revolutionizing personalized medicine in India. What are the ethical, legal, and social implications associated with large-scale genomic data collection? |


