Micro, Small, and Medium-Sized Enterprises (MSMEs) are crucial to India’s economy, contributing 30% to the GDP and employing 110 million people. Despite their significant role, MSMEs face numerous challenges, including limited funding, outdated technology, and regulatory hurdles. Adopting sustainable practices can help MSMEs overcome these issues, reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance their market reputation.
Origin of the Article
This editorial is based on “How MSMEs can benefit by adopting sustainable practices,” published in The Indian Express on June 28, 2024. The article discusses the importance of sustainable practices for MSMEs.
Relevancy for UPSC Students
Understanding the role of MSMEs and their challenges is crucial for UPSC aspirants, as it relates to GS Paper 3 on the Indian Economy and Issues Related to Planning and MSMEs. Knowledge of sustainable practices will help in answering questions related to economic development and environmental sustainability, important areas in the UPSC syllabus.

Why in News
The focus on MSMEs adopting sustainable practices is significant due to their crucial role in the Indian economy, contributing 30% to GDP and employing 110 million people. Given the sector’s substantial environmental impact, integrating sustainable practices aligns with India’s broader goals of sustainable development.
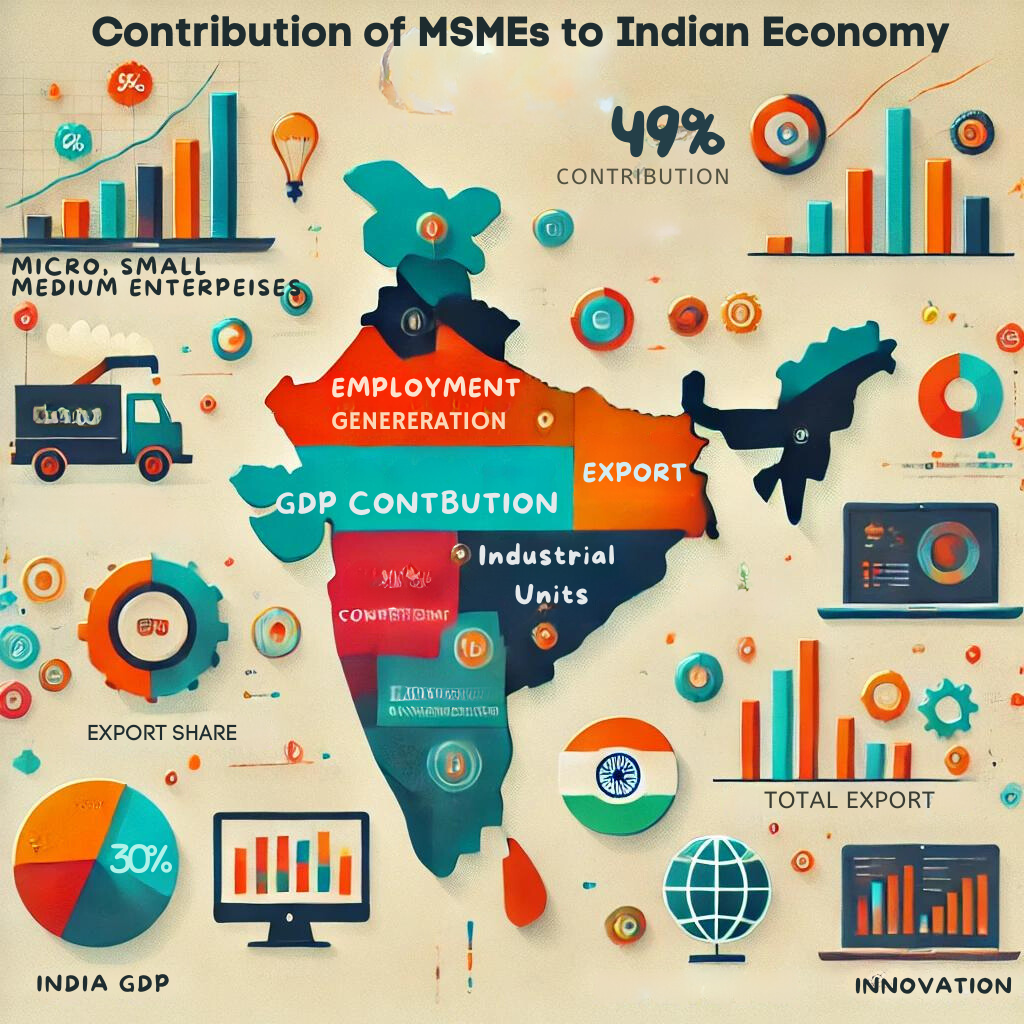
Contribution of MSMEs to the Indian Economy
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are the backbone of the Indian economy. They play a crucial role in employment creation, GDP contribution, and exports. These enterprises foster economic growth by providing jobs to millions and contributing significantly to national income and global trade.
Employment Creation
MSMEs offer diverse employment opportunities in both rural and urban areas. According to Udyam portal data, around 1.28 crore MSME-registered industries employed 9.31 crore people in December 2022, including 2.18 crore women employees. This sector is vital for job creation, employing approximately 110 million people.
GDP Contribution
MSMEs contribute about 30% to India’s GDP, making them a significant economic sector. Their role in the economy cannot be overstated, as they support diverse industries and drive economic development, enhancing the overall economic stability of the country.
Export Contribution
MSMEs contribute 49% to India’s total exports, underscoring their importance in global trade. Small businesses play a critical role in exporting goods and services, thereby boosting the country’s foreign exchange reserves and global economic standing.
Industrial Units
Small businesses own 96% of all industrial units in India. This widespread presence underscores their importance in the overall manufacturing production, contributing significantly to the country’s industrial output and economic resilience.
Current Status and Challenges for MSMEs in India
The current scenario for MSMEs in India is a mix of growth and challenges. While the sector is expanding, it faces numerous obstacles that impede its full potential and sustainability.
Restricted Access to Resources
MSMEs often struggle with limited access to essential resources such as funding, technology, and skills. These constraints hinder their growth and competitiveness, making it difficult for them to scale operations and innovate.
Insufficient Infrastructure
Poor infrastructure is a significant impediment to MSME growth. Inadequate facilities and logistical challenges often stifle productivity and increase operational costs, affecting the overall efficiency of the sector.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Onerous regulatory requirements and compliance burdens pose substantial challenges for MSMEs. Navigating through complex regulations can be time-consuming and costly, diverting resources away from productive activities.
Productivity and Competitiveness
Low productivity and competitiveness are major issues for MSMEs. Limited access to modern technology and skilled labor often results in suboptimal production processes and reduced market competitiveness.
Climate-Related Risks
Climate-related heat stress and other environmental risks exert enormous pressure on MSMEs, impacting infrastructure, operations, and resources. These challenges can lead to financial crises, job losses, and migration, exacerbating the sector’s vulnerabilities.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
MSMEs contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, producing around 110 million tonnes of CO2 annually. This environmental impact highlights the need for sustainable practices to mitigate their carbon footprint and enhance environmental sustainability.
Measures to Overcome Challenges faced by MSMEs
Adopting sustainable and responsible business practices is crucial for MSMEs to overcome various challenges and ensure long-term growth and stability.
Adoption of ESG Framework
MSMEs should adopt the Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework to manage energy, waste, and carbon emissions. This approach fosters sustainability and aligns business practices with global environmental standards.
National Guidelines for Responsible Business Conduct (NGRBC)
Following the NGRBC principles can help MSMEs align their business processes with responsible and sustainable practices. These guidelines serve as a foundation for ethical and sustainable business conduct.
Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR)
Aligning with SEBI’s BRSR for listed businesses can enhance transparency and accountability. This practice ensures that businesses meet stakeholder expectations and adhere to sustainability norms.
Stakeholder Expectations
Meeting stakeholder expectations through sustainable practices is vital for MSMEs. This approach not only improves brand reputation but also enhances business value and societal impact.
Environmental and Social Impact
Adopting sustainable practices positively impacts the environment and society. It enhances corporate value and aligns business operations with broader societal goals, fostering a more inclusive and sustainable economy.
Government and Stakeholder Role
The government and stakeholders play a crucial role in raising awareness and providing resources to MSMEs. Initiatives to share best practices, offer training, and provide necessary resources are essential for promoting sustainable business practices.

Way Forward
MSMEs can significantly benefit from adopting sustainable practices, with support from larger corporations and government initiatives playing a pivotal role in facilitating this transition.
Supply Chain Collaboration
Collaborating with supply chain partners can drive sustainability improvements throughout the value chain. Such partnerships enhance overall efficiency and promote responsible business practices.
Support from Larger Corporations
Larger corporations can assist MSMEs by offering training, technical assistance, and financing. This support helps MSMEs integrate sustainable practices and improve their operational capabilities.
GreenCo Rating System
The CII’s GreenCo Rating System promotes sustainability by assessing firms based on their environmental performance. This rating system encourages businesses to adopt green practices and enhance their environmental stewardship.
Cost and Efficiency Benefits
Sustainable practices can lead to cost savings and increased efficiency for MSMEs. These benefits provide a competitive advantage by reducing operational costs and improving productivity.
Government Promotion
Government initiatives are crucial in promoting sustainable practices among MSMEs. Support from the government ensures that businesses receive the necessary resources and recognition for their efforts.
Ratings and Recognition
Ratings like the IGBC Green Factory Building Rating System can attract customers and investors who value sustainability. Such recognition sets businesses apart from competitors and enhances their market appeal.
PESTEL Analysis
| Political: Government support and regulations play a significant role in encouraging MSMEs to adopt sustainable practices. Initiatives like the National Guidelines for Responsible Business Conduct (NGRBC) and government-backed financing programs can help MSMEs navigate strict regulatory environments. Political stability and policy continuity are crucial for MSMEs to invest confidently in sustainable infrastructure. Economic: MSMEs contribute about 30% to India’s GDP and provide jobs to 110 million people. Adopting sustainable practices could enhance their economic stability by reducing operational costs and attracting investments through improved compliance with global sustainability standards. However, limited access to funding remains a major challenge, necessitating targeted financial products and subsidies. Social: As significant employers, MSMEs have a direct impact on community welfare. Implementing sustainable practices can lead to safer working conditions and better community relations. Social acceptance and demand for responsible business conduct can drive MSMEs to adopt such practices more broadly. Technological: Leveraging technology for sustainable business operations, such as energy-efficient processes and waste management systems, is essential. However, MSMEs often face barriers in accessing advanced technologies, underscoring the need for partnerships with larger corporations and technology providers. Environmental: MSMEs are responsible for a substantial portion of industrial emissions. By adopting the ESG framework and other sustainability measures, they can significantly reduce their environmental footprint. This is increasingly important as regulatory pressures mount in response to global climate change challenges. Legal: Compliance with existing and emerging environmental regulations is a critical factor for MSMEs. The Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) can help them align with future legal requirements, reducing the risk of penalties and enhancing their competitiveness in a stringent legal framework. |
Conclusion
The adoption of sustainable practices by MSMEs is not just a strategic move but a necessity in today’s world. As future civil servants, understanding and promoting these practices can drive economic growth while safeguarding our environment. It is crucial to envision a future where MSMEs thrive sustainably, contributing to India’s development and aligning with global sustainability goals.
| UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs) Mains Q. Microfinance as an anti-poverty vaccine, aimed at asset creation and income security of the poor, has failed to deliver in many parts of the country. Examine critically. (GS-III, 2022) Q. Evaluate the impact of implementing the Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework on the operational efficiency and market reputation of MSMEs in India. What are the potential benefits and challenges associated with this framework? |

