The Middle East is crucial for India due to its energy security needs, with countries like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and the UAE being major suppliers of crude oil and natural gas. Any disruption in supply or price fluctuations directly impacts India’s economy. India also collaborates with Middle Eastern countries on counter-terrorism, enhancing intelligence sharing, and dismantling terrorist networks. The significant Indian diaspora in the region contributes to local economies and sends substantial remittances back to India. Deep cultural and historical ties further strengthen the relationship, reflected in shared traditions and recent initiatives like the India-Arab League media symposium.
India’s active involvement in developing regional connectivity and infrastructure projects, such as the Chabahar port and the International North-South Transport Corridor, enhances its access to Central Asia and Europe. Multilateral engagement with forums like the United Nations and the Organization of Islamic Cooperation helps India build coalitions and enhance its global standing. The recent escalation between Israel and Iran-backed forces, characterized by a vicious cycle of violence and retaliation, underscores the region’s complex dynamics. This draw-out instability weakens the region and has global effects, including oil price changes and increasing geopolitical tensions. Given its strategic location, energy security interests, and growing economic ties, India has a vital stake in a stable Middle East.
| GS Paper | General Studies II |
| Topics for UPSC Prelims | Middle East, India’s crude oil and natural gas requirements, Chabahar port project, International North-South Transport Corridor, India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, Organization of Islamic Cooperation, Arab League, UNSC, Israeli-Palestinian conflict, Abraham Accords, India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement |
| Topics for UPSC Mains | Significance of the Middle East for India, Issues Related to Middle East and Impact on India. |
Origin of the Article
This editorial is based on “A widening war in the Middle East,” published in The Indian Express on August 7, 2024. The article highlights the escalating conflict in the Middle East, driven by recent assassinations of Iranian proxy leaders, with no significant political outcomes despite the intense violence and widespread social and economic repercussions for both Israel and Iran.
Relevancy for UPSC Students
Understanding the complexities of the Middle East is crucial for UPSC aspirants. It aligns with the UPSC syllabus under topics like International Relations, Bilateral Groupings, and Global Security. Knowledge of this region aids in comprehending India’s foreign policy, energy security, and global diplomatic strategies.

Why in News
The recent escalation in the Middle East involving Israel and Iran-backed forces has brought the region into sharp focus for UPSC aspirants. The conflict’s impact on global oil prices, energy security, and geopolitical stability underscores its significance for India. Previous UPSC questions have emphasized understanding the region’s complex dynamics, making it crucial for candidates to grasp these developments comprehensively.
Significance of the Middle East for India
The Middle East holds immense importance for India, given its strategic location, energy resources, and deep-rooted cultural ties. The region significantly impacts India’s energy security, trade relations, and geopolitical interests. It also serves as a crucial partner in counter-terrorism efforts and hosts a large Indian diaspora contributing to remittance flows. Furthermore, India’s engagement in regional connectivity projects and multilateral forums enhances its global influence.
Energy Security and Trade Ties
The Middle East is vital for India’s energy security, supplying a substantial portion of its crude oil and natural gas. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and the UAE are key energy partners. According to the World Energy Outlook 2021, India’s energy consumption is set to rise significantly by 2050, making stable Middle Eastern energy supplies crucial for its growing economy. Disruptions in this supply can severely impact India’s economic performance and inflation levels.
Counter-Terrorism Cooperation
India collaborates with Middle Eastern nations like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Israel to combat terrorism. This cooperation includes intelligence sharing and the import of military equipment, aiding in the disruption of terrorist financing and logistics. Over the last decade, India has imported significant military equipment from Israel, enhancing its counter-terrorism capabilities and contributing to regional security.
Diaspora and Remittance Flows
The Middle East is home to over 66% of India’s non-resident population, mainly in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, and Bahrain. This diaspora is a major source of remittances, bolstering India’s economy. Ensuring their welfare and security is a priority, as evidenced by India’s proactive measures in various situations, including the recent case of former Indian Navy veterans in Qatar.
Cultural and Civilizational Linkages
India and the Middle East share deep cultural and historical ties, reflected in ancient trade routes and contemporary cultural exchanges. Initiatives like the India-Arab League media symposium and the establishment of the BAPS Hindu Mandir in Abu Dhabi exemplify the ongoing efforts to strengthen these connections, fostering a rich and multifaceted relationship.
Regional Connectivity and Infrastructure
India’s involvement in regional connectivity projects like the Chabahar port in Iran and the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) is pivotal. These initiatives enhance India’s access to Central Asia and Europe, boosting trade and reducing dependency on Pakistan for regional connectivity. Such projects also expand India’s strategic influence in the Middle East.
Multilateral Engagement and Global Influence
India’s engagement with multilateral forums like the United Nations, OIC, and the Arab League amplifies its global influence. Active participation helps India navigate complex regional dynamics, build coalitions, and enhance its bargaining power on strategic issues. This engagement also supports India’s stance on domestic issues like the Kashmir dispute, leveraging support from like-minded OIC countries.

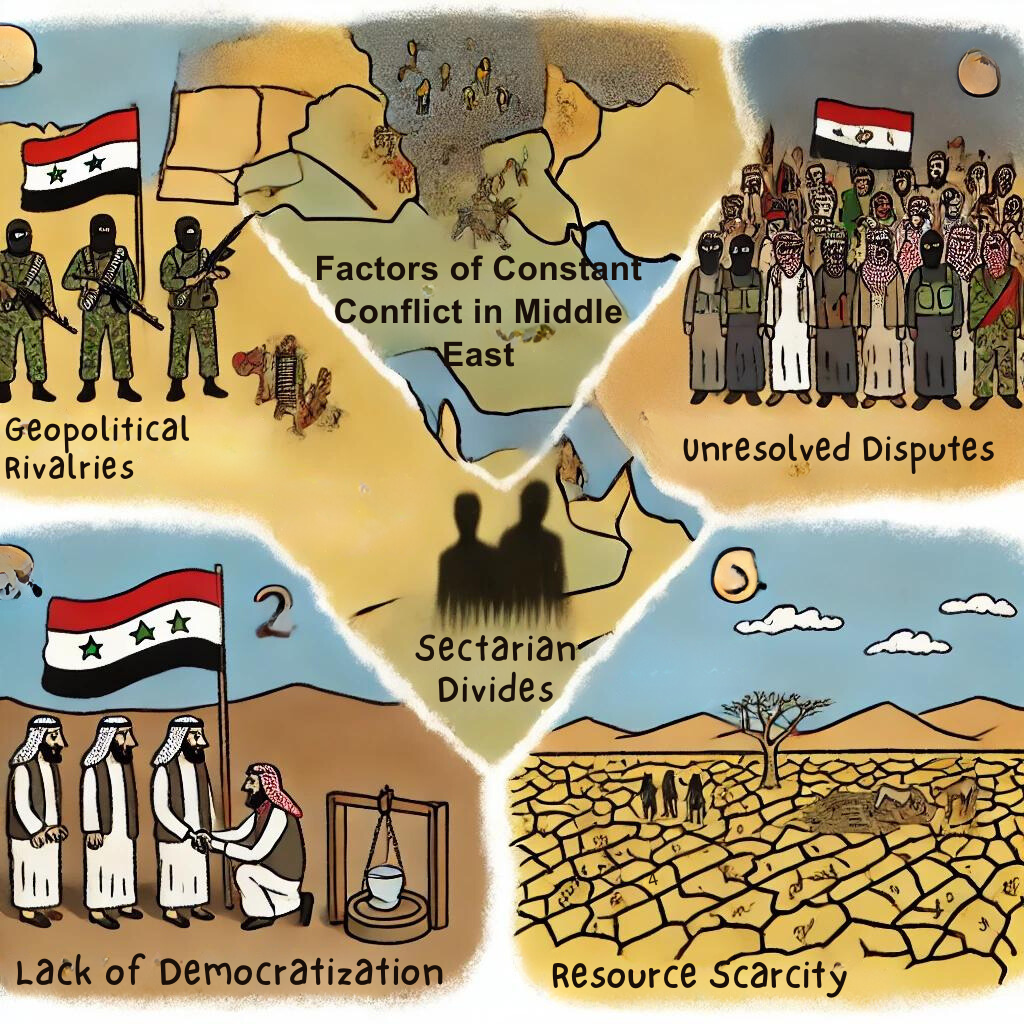
Constant Conflict and Instability in the Middle East
The Middle East is plagued by persistent conflict and instability, driven by geopolitical rivalries, protracted disputes, and sectarian divides. Authoritarian regimes and resource scarcity further exacerbate tensions, making the region a hotspot for international conflicts and interventions. These factors collectively hinder peace and development, impacting not just the region but the global community.
Geopolitical Rivalries and Proxy Conflicts
The Middle East is a battleground for geopolitical rivalries involving Iran, Saudi Arabia, Israel, Turkey, and the USA. These rivalries often manifest in proxy wars, such as the conflict in Yemen, where Iran-backed Houthi rebels clash with a Saudi-led coalition. The involvement of external actors and the lack of balance of power perpetuate instability and violence in the region.
Protracted Conflicts and Unresolved Disputes
Long-standing conflicts like the Israeli-Palestinian issue resist resolution due to external interventions and the rigid positions of the parties involved. Initiatives like the Abraham Accords, which aimed at normalizing relations between Israel and several Arab nations, face setbacks, reversing earlier progress and perpetuating the region’s instability.
Sectarian Divides and Identity Politics
Sectarian divides, particularly between Sunni and Shia Muslims, fuel numerous conflicts in the Middle East. Political actors exploit these tensions to consolidate power, leading to political fragmentation and radical ideologies. The Syrian civil war exemplifies how sectarian divides can escalate into violent confrontations, destabilizing the region further.
Authoritarian Regimes and Lack of Democratization
Many Middle Eastern countries are governed by authoritarian regimes that prioritize regime security over citizen welfare. Repressive measures, lack of democratic reforms, and political marginalization lead to uprisings, such as the Arab Spring. The failure to address root causes like economic inequality and corruption perpetuates the cycle of instability.
Resource Scarcity and Environmental Challenges
The Middle East faces severe environmental challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and the impacts of climate change. Resource constraints exacerbate existing tensions, fueling conflicts over limited resources. The dispute over the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam highlights how environmental issues can escalate regional tensions.
Strengthening India-Middle East Relations
India can enhance its relationship with the Middle East through a balanced foreign policy, economic engagement, and defense cooperation. By positioning itself as a neutral mediator and reliable partner, India can foster regional stability and build robust economic and strategic ties. Promoting mutual tourism and enhancing disaster management cooperation can further strengthen these relations.
Balanced and Nuanced Foreign Policy Approach
India’s balanced diplomatic approach in the Middle East is crucial. By avoiding taking sides in regional rivalries, India can act as a neutral mediator, promoting dialogue and stability. This approach is evident in India’s stance during the Israel-Hamas conflict and its efforts to maintain communication with Iran despite US sanctions.
Enhancing Economic Engagement and Interdependence
Strengthening economic ties through trade and investment is vital for regional stability. Initiatives like the India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement exemplify mutually beneficial relationships. India’s digital influence can also be deepened by leveraging its diaspora to promote digital payment systems in the region.
Strengthening Defense and Security Cooperation
Enhancing defense and security cooperation through joint military exercises and co-development of defense technologies can bolster regional stability. India’s role as a reliable security partner can deter aggression and build trust, contributing to a safer Middle Eastern landscape.
Middle East as Link Between the Global North and Global South
India’s position as a leading voice of the Global South enables it to mediate between Middle Eastern and Western powers. Advocating for developing nations’ interests and fostering South-South cooperation can create inclusive platforms for dialogue and negotiation, promoting a more equitable global order.
Promoting Mutual Tourism
India can boost tourism in the Middle East through collaborative marketing campaigns and streamlined visa processes. Initiatives like the “Visit Saudi” campaign during the IPL highlight the potential for mutual tourism, strengthening cultural and economic ties between the regions.
Strengthening Disaster Management and Humanitarian Assistance
India can enhance its role in disaster management and humanitarian assistance in the Middle East. Coordinating with regional organizations to develop early warning systems and provide rapid relief during crises can position India as a reliable partner, as demonstrated by Operation Dost in Turkey and Syria.
PESTEL Analysis
| Political: India’s political engagement in the Middle East is crucial due to its strategic interests. The region’s instability, marked by geopolitical rivalries and sectarian conflicts, requires India to maintain a balanced foreign policy, promoting dialogue and mediation while enhancing defense and security cooperation. Economic: The Middle East is a vital energy source for India, with countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE being key suppliers of crude oil and natural gas. Economic disruptions due to regional conflicts or fluctuations in oil prices can significantly impact India’s economy. Social: India has a large diaspora in the Middle East, contributing to remittance flows and cultural exchange. Ensuring their welfare and security is a priority, along with fostering deeper cultural and civilizational linkages with the region. Technological: India’s involvement in regional connectivity projects, like the Chabahar port, enhances technological and infrastructure linkages, facilitating access to Central Asia and Europe. Environmental: The Middle East faces resource scarcity and environmental challenges, such as water scarcity and climate change, which could exacerbate regional tensions, indirectly affecting India’s interests. Legal: India’s engagement with Middle Eastern nations through multilateral platforms like the UN and the Arab League is vital for global diplomacy, ensuring legal frameworks that support mutual economic and security interests. |
Conclusion
The Middle East remains a region of vital importance for India, with deep historical, cultural, and economic ties. By leveraging its position as a leading voice of the Global South, India can play a constructive role in bridging the divide between the Middle Eastern countries and the traditional global powers, while also addressing shared challenges like terrorism and climate change.
| UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs) Mains Q. Discuss the impediments India is facing in its pursuit of a permanent seat in UN Security Council. (GS Paper II, 2015). Q. Analyze the implications of the ongoing war in the Middle East, particularly between Israel and Iran, on India’s crude oil and natural gas requirements. What measures should India take to secure its energy needs in light of this instability? |


